Definition
Environmental Impact Assessment or EIA is the process through which an environmental impact of a proposed development is evaluated. It takes into consideration the socio-economic, cultural, and human health impacts, both beneficial and adverse. EIA is a tool used to assess the positive and negative environmental, economic, and social impacts of a project. This is used to predict the environmental impacts of a project in the pre-planning stage itself so that decisions can be taken to reduce the adverse impacts. EIA had started in India in 1976-77.
Significance and scope of impact assessment,
EIA plays a crucial role in protecting the environment and promoting sustainable development. By identifying potential impacts and proposing mitigation measures, it ensures that projects are designed and implemented in an environmentally responsible manner.
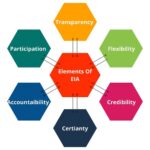
The process helps identify potential environmental impacts at an early stage, allowing for appropriate measures to be taken to prevent or minimize adverse effects. It enables the integration of environmental considerations into project planning and decision-making. EIA promotes public participation, allowing affected communities and stakeholders to voice their concerns and contribute to the decision-making process. This transparency enhances public trust and accountability.
Lastly, EIA ensures that environmental considerations are integrated into the planning and design of projects from the early stages. Doing so helps avoid costly and environmentally damaging modifications later in the project lifecycle.
major steps in impact assessment procedure.
The EIA process comprises several key steps to ensure a comprehensive assessment of potential environmental impacts. These steps include screening and scoping, baseline data collection, impact prediction, mitigation measures and alternatives identification, public consultation, and the review and decision-making process.
- Screening and Scoping Processes in EIA
The screening process involves determining whether a project requires an EIA based on size, nature, and potential impacts. Scoping involves identifying the key issues and potential impacts that should be addressed in the EIA study.
- Baseline Data Collection and Impact Prediction Techniques
Baseline data collection is crucial in understanding the existing environmental conditions before a project is implemented. This includes collecting information on air quality, water quality, soil conditions, biodiversity, and socio-economic aspects. Then, based on the collected baseline data, impact prediction techniques are used to assess how the proposed project may affect the environment.
- Mitigation Measures and Alternatives Assessment
Once potential impacts are identified, mitigation measures are proposed to minimize or eliminate adverse effects. Alternatives assessment involves evaluating different project options or locations to identify those with lesser environmental impacts.
- Public Consultation and Participation in EIA
Public consultation is a fundamental aspect of the EIA process, allowing affected communities and other stakeholders to provide input and raise concerns. This ensures that the decision-making process is transparent and considers diverse perspectives.
- Review and Decision-Making Process
The relevant authorities review the EIA report, including the findings from the assessment and proposed mitigation measures. Based on the report and public inputs, a decision is made regarding the project’s approval, rejection, or approval with conditions.
Impacts of Environmental Impact Assessment
EIA considers various components to assess a project’s potential environmental impacts comprehensively. It evaluates the
- Physical impacts such as land use changes and habitat loss
- Biological impacts such as effects on flora and fauna and
- Social impacts such as displacement of communities and changes in livelihoods
EIA assesses a project’s potential impacts on air quality, including emissions of pollutants. It also considers impacts on water resources, such as water availability and quality changes. Additionally, soil quality is assessed to determine potential impacts on agricultural productivity and soil erosion. The process evaluates potential impacts on biodiversity, including terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. In addition, it considers the conservation of endangered species, habitat fragmentation, and ecosystem services.
EIA also includes assessing socio-economic aspects, such as impacts on local communities, employment, and infrastructure. It also examines potential health impacts on workers and nearby communities due to project activities.
What are Advantages of EIA?
By using EIA both environmental and economic benefits can be achieved, such as:
- Reduced cost and time of project implementation and design,
- Avoided treatment/clean-up costs and impacts of laws and regulations.
- Lays base for environmentally sound projects;
- Greater awareness of environmental legislation;
- Protection of Environment.
- Optimum utilization of resources(balance between development and Environmental protection).
- Informs decision makers.
- EIA reports are a critical component of India’s environmental decision-making process.
- It acts as a detailed study of the potential impacts of proposed projects.
- It helps in predicting environmental impacts at an early stage in project planning and design.
- Based on these reports, the Environment Ministry or other relevant regulatory bodies may or may not grant approval to a project.
- The EIA reports are also important to define measures that the project could take in order to contain or offset project impacts.
- EIA-based approvals for most projects also involve the process of conducting public hearings, so that who are likely to be affected can be taken on board before approving the project.
- EIA links environment with development.
- The goal is to ensure environmentally safe and sustainable development.
Continue Reading: WHAT ARE THE KEY ELEMENTS OF AN ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT EIA?
ATM (Aid to Memory) : Multiple Choice Questions





3 thoughts on “Environmental Impact Assessment”